Hasselman department of materials engineering virginia polytechnic institute and state university blacksburg va 24061 u s a received october 7 1984 abstract an overview is presented of the current understanding of the variables which affect the thermal stress failure of.
Ceramics stress of instantaneous temperature change.
Quenching polymer concentration method were all 500 c s 1 i e.
Plane strain conditions give the lowest.
The experimental ν max c measured at three heating temperature 500 c 600 c 700 c using residual strength vs.
Request pdf an aqueous polymer quenching medium for instantaneous thermal shock cooling rate study of ceramic materials an aqueous polymer quenching technique combing with a thermocouple real.
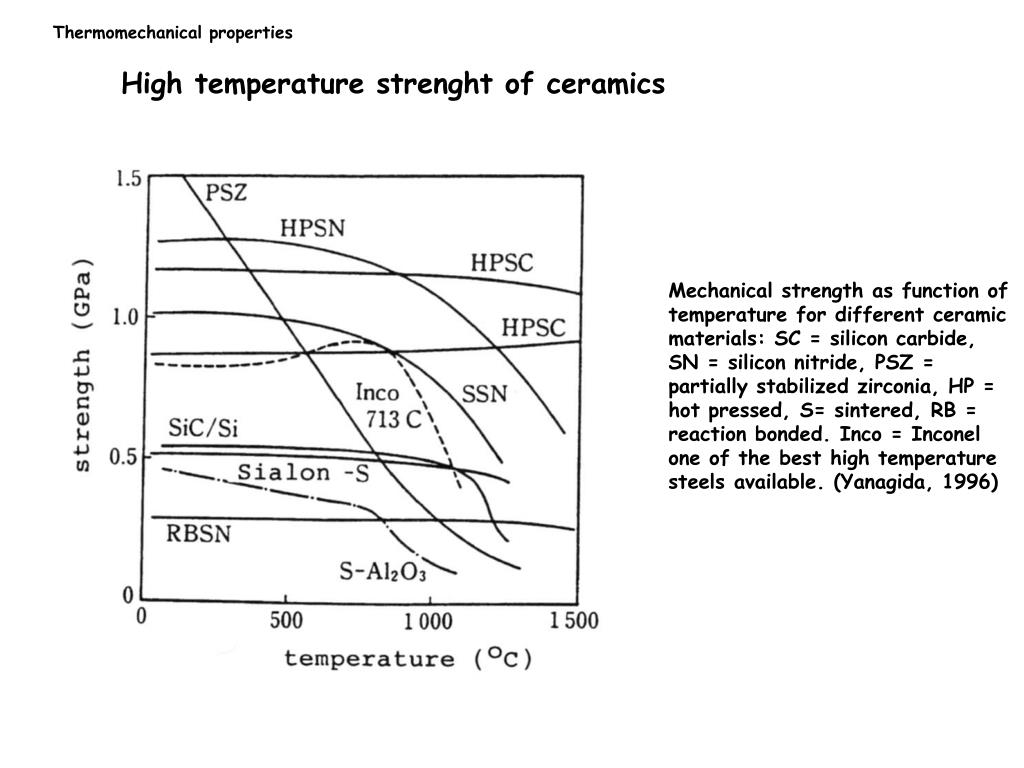
Mechanical properties versus melting temperature.
Sometimes even monocrystalline materials such as diamond and sapphire are erroneously included under the term ceramics.
Kingery ceramics division department of metallurgy massachusetts lnstihrte of technology cambridge massachusetts the sources and calculation of thermal stresses are considered together with the factors in volved in thermal stress resistance factors.
In mechanics and thermodynamics thermal stress is mechanical stress created by any change in temperature of a material.
Ceramics 30 350 gpa metals 50 200 gpa polymers 50 gpa 2.
A component s thickness affects the constraint conditions at the tip of a crack with thin components having plane stress conditions and thick components having plane strain conditions.
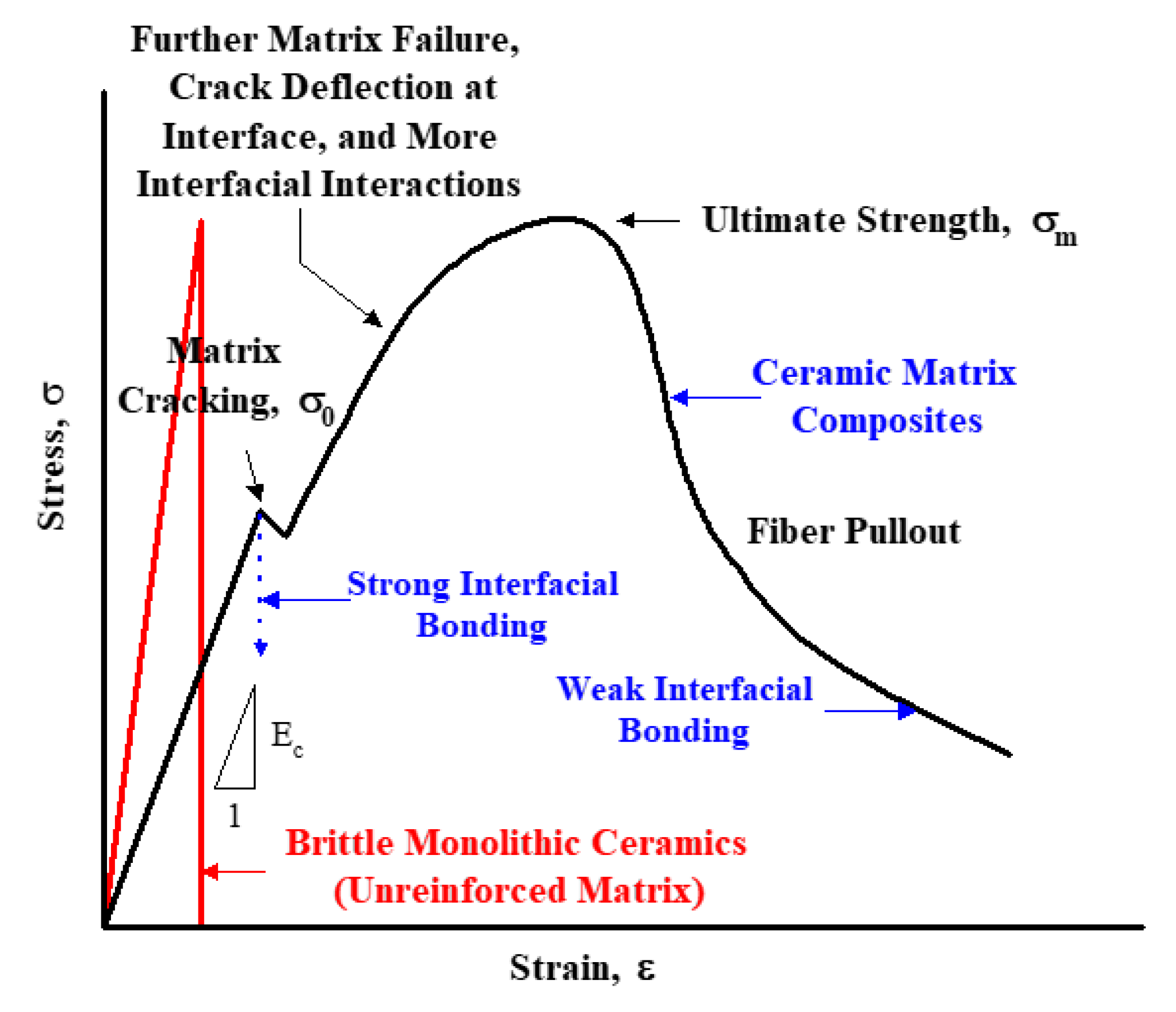
Materials science and engineering 71 1985 251 264 251 thermal stress resistance of engineering ceramics d.
Properties depend both on temperature and degree of crystallinity.
Factors affecting thermal stress resistance of ceramic materials by w.
σ dt e ε e dl l o e α l o dt l o e α dt 4 where.
The maximum permitted instantaneous temperature gradient generated during aqueous silicone oil quenching condition should not exceed 500 c s 1.
Temperature gradients thermal expansion or contraction and thermal shocks are things that can lead to thermal stress.
When restricted expansion is converted to stress then 1 2 and 3 can be combined to.
These stresses can lead to fracturing or plastic deformation depending on the other variables of heating which include material types and constraints.
σ dt stress due to change in temperature pa n m 2 psi axial force.
Polycrystalline materials are formed by multiple.
In materials science fracture toughness is the critical stress intensity factor of a sharp crack where propagation of the crack suddenly becomes rapid and unlimited.
Properties affecting thermal stress resistance of.
The ceramic s achilles heel is its resistance to fracturing however which plummets by almost 90 per cent when the material experiences sudden changes in temperature such as being heated above.
The properties of ceramics however also depend on their microstructure.
The axial force acted by the restricted bar due to change in temperature can be expressed as.